软考程序员应用技术科目(下午考试)题目总结
撰写于 2025年5月24日
修改于 2025年5月24日
分类
考试
标签
软考
views
程序员考试的应用技术科目,在之前使用笔试考试时考试是在下午进行,也叫“下午考试”。一共六个题目,前四个为必做题,后面两个题为二选一,各题题目如下:
第 1 题:流程图填空题,一般是伪代码填空
第 2 至第 4 题,C 语言程序代码题
最后两题:均为面向对象编程题,二选一,根据语言分为 C++和 Java 题。
本文中,使用 202011-4 表示 2020 年下半年考试中应用技术的第 4 题,考试原题参考这里 。
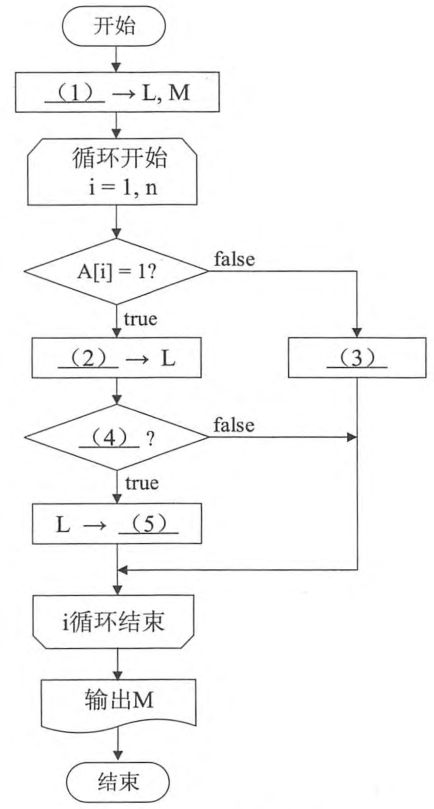
第 1 题:流程图 样题 202011-1 下面流程图所示算法的功能是:在一个二进制位串中,求出连续的“1”构成的所有子串的最大长度 M。例如,对于二进制位串 0100111011110,M=4。
该算法中,将长度为 n 的二进制位串的各位数字,按照从左到右的顺序依次存放在数组 A[1..n]。在对各个二进制位扫描的过程中,变量 L 动态地记录连续“1”的个数。
1 2 3 4 5 (1) 0 (2) L+1或等效形式 (3) 0→L或等效形式 (4) L>M或L≥M或等效形式 (5) M
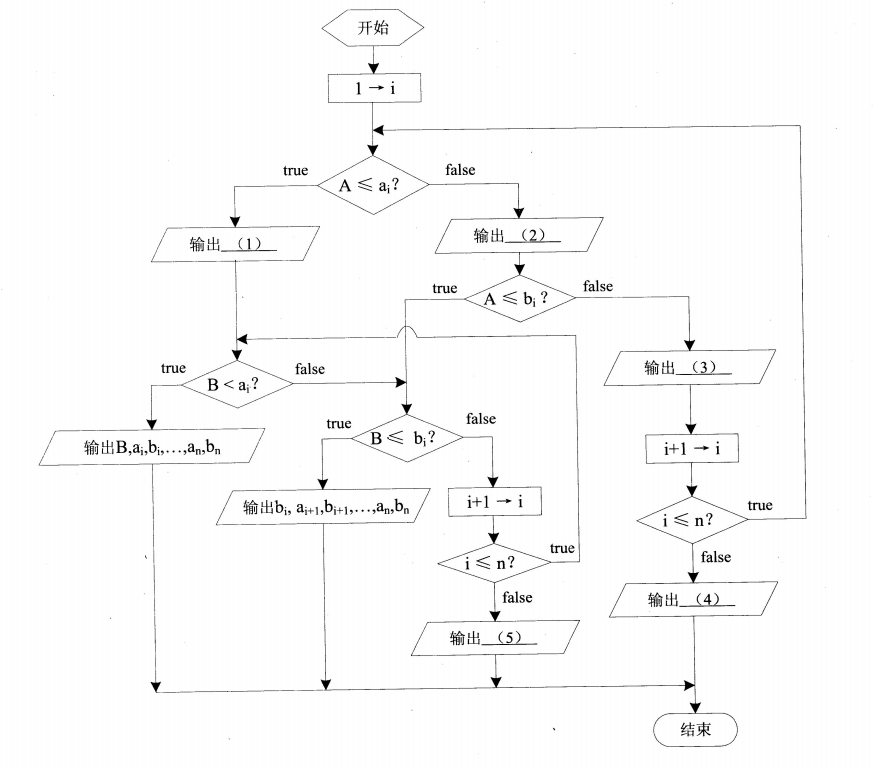
201811-1 设[a1b1],[a2,b2],…,[an,bn]是数轴上从左到右排列的 n 个互不重叠的区间(a1 < b1 < a2 < b2… < an < bn )。以下流程图将一个新的区间[A,B](A < B)添加到上述区间集,形成新的从左到右排列的若干个互不重叠的区间(若 A、B 落在原有的两个区间,则以原有区间最左端点和最右端点为基准,形成新的区间),最后依次输出这些区间的端点。
1 2 3 4 5 (1) A (2) ai (3) bi (4) A,B (5) B
第 2 至 4 题:代码填空题 主要考查形式包括以下几种:
给出代码运行结果
填写各种边界条件、判断条件
考查 C 语言中基本函数用法,比如 scanf (201805-4) fabs(202011-2)
自定义函数的调用
指针的使用
链表的使用
运行结果题 题目给出代码,问题给定输出,答案预测输出。代表题目有:
201905-1
201805-3
201711-2
201811-2 阅读以下 C 代码,回答问题 1 和问题 2,将解答填入答题纸的对应栏内。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main () { int a,tmp,b=0 ; scanf ("%d" ,&a); tmp=a<0 ?-a:a; while (tmp){ b=b*10 +tmp%10 ; tmp=tmp/10 ; } if (a==b||-a==b) printf ("Palindromic number.\n" ); printf ("a=%d b=%d\n" ,a,b); return 0 ; } #include <stdio.h> int main () { char grade; int points; for (grade='A' ;grade<'F' ;grade++){ switch (grade){ case 'A' :points=4 ;break ; case 'B' :points=3 ; case 'C' :points=2 ; case 'D' :points=1 ;break ; case 'E' : case 'W' :points=0 ; } if (points>0 ) printf ("Passed,point=%d\n" ,points); else printf ("Failed\n" ); } return 0 ; }
【问题 1】
【问题 2】
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 【问题1】 输入-1331的结果是: Palindromic number. a=-1331 b=1331 输入795的结果是: a=795 b=597 【问题2】 输出结果是: Passed,point=4 Passed,point=1 Passed,point=1 Passed,point=1 Failed
填写各种边界条件、判断条件 这类题目很多,或者说大部分题目都涉及到这个考点,但对应真正写过代码的人来讲也是最简单的题目。
201811-3
201811-4
201905-3
201905-4
201711-2
201811-3 【说明】0.5=75.00 元;某户 B 用电量为 280 度,其电费为 180 0.5+(280-180)0.55=145.00 元;某户 C 用电量为 450 度,其电费为 180 0.5+(360-180)*0.55+(450-360)*0.7=90.0+99.0+63.0=252.00 元。
下面程序运行时读入 m(m>0)个住户某月的用电量,计算该月每户应缴的电费并输出,同时找出这 m 个住户中该月的最大用电量和最小用电量。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <stdio.h> #define MAXQT 100000 double proc (int qt) { double fee=0.0 ; if ( (1 ) ) fee=qt*0.5 ; else if ( (2 ) ) fee=180 *0.5 +(qt-180 )*0.55 ; else fee= (3 ) ; return fee; } int main () { int m ; int qt , minimun = MAXQT , maximum = 0 ; scanf ( "%d" ,&m); while (m>0 ){ scanf ( "%d" , &qt ) ; if (qt<0 ‖ qt>MAXQT ) continue ; printf ( "%.21f\n " , proc(qt) ) ; if ( (4 ) ) minimum=qt; else if ( (5 ) ) maximum=qt; (6 ) ; } printf ( "maximum=%d,minimum=%d\n " ,maximum,minimum); return 0 ; }
答案
1 2 3 4 5 6 (1) qt<=180 (2) qt<=360 (3) 180 * 0.5 + (360-180) * 0.55 + ( qt - 360 ) * 0.7 或 0.7 * qt - 63 (4) minimum>qt (5) maximum<qt (6) m--
考查 C 语言中基本函数用法 需要对 C 语言或者类 C 语言有一定了解才更有助于作答。
fabs(202011-2)scanf (201805-4)
202011-2 答案
1 2 3 4 5 (1) fabs(x)<=1e-6 或fabs(x)<=0.00001x==0.0或等效形式 (2) x2 (3) x/(x1*x1)或等效形式 (4) (x2-x1)/x1或等效形式 (5) x+=0.1或x=x+0.1或等效形式
201805-4 【说明】
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 include <stdio.h> define NUMBER 100 int isValid (const char s1) ; char toLower (char ch) ; int usr_strcmp (char s1, char s2) ; void usr_strcpy (char s1,const char s2) ; int main () { char word[32 ]; char maxWord[32 ]="" , minWord[32 ] ="" ; int numWord=0 ; while (numWord < NUMBER) { scanf ("%s" , (1 ) ); if (isValid(word)) { if (0 ==numWord) {usr_strcpy(minWord,word);usr_strcpy(maxWord,word);} numWord++; if ( (2 ) >0 ) usr_strcpy(maxWord, word); else if ( (3 ) <0 ) usr_strcpy(minWord,word); } } printf ("maxWord=%s minWord=%s\n" ,maxWord,minWord); return 0 ; } int isValid (const chars) { for (; s ; s++) if (!(s>='a' && s<='z' ) && !(s>='A' && s<='Z' )) return 0 ; return 1 ; } char toLower (char ch) { if (ch>='A' && ch<='Z' ) ch= (4 ) +'a' ; return ch; } int usr_strcmp (char s1,char s2) { for (; (5 ) ;) { if (toLower(s1)==toLower(s2)) {s1++,s2++;} else break ; } return (toLower(s1) - toLower(s2)); } void usr_strcpy (char s1,const char s2) { for (; (6 ) ;) s1++= s2++; s1='\0' ; }
答案
1 2 3 4 5 6 (1)word (2)usr_strcmp(word, maxWord) (3)usr_strcmp(word, minWord) (4)ch-'A' (5)s1!='\0'&&s2!='\0'或s1||s2等价表示 (6)s2!='\0'或s2等价表示
指针、链表的使用
202011-3
202011-4
201705-4
201511-4
201511-4 函数 GetListElemPtr(LinkList L,int i)的功能是查找含头结点单链表的第 i 个元素。若找到,则返回指向该结点的指针,否则返回空指针。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 #define SUCCESS 0 #define ERROR -1 typedef int Status;typedef int ElemType;typedef struct Node { ElemType data; struct Node next ; } Node , LinkList; LinkList GetListElemPtr (LinkList L ,int i) { LinkList p; int k; if (i<1 ∣∣ !L ∣∣ !L->next) return NULL ; k = 1 ; P = L->next; while (p && (1 ) ) { (2 ) ; ++k; } return p; } Status DelListElem (LinkList L ,int i ,ElemType e) { LinkList p,q; if (i==1 ) (3 ) ; else p = GetListElemPtr(L ,i-1 ); if (!p ∣∣ !p->next) return ERROR; q = (4 ) ; p->next = q->next; (5 ) ; free (q); return SUCCESS; }
答案
1 2 3 4 5 (1) k<i (2)p = p->next (3)p=L (4)p->next (5)*e = q->data
201705-4 【说明】
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 enum {typedef int KeyType;typedef struct QNode { KeyType data; Struct QNodenext; }QNode,LinkQueue; Typedef struct { int size; Link:Queue rear; } Queue; int EnQueue (QueueQ,KeyType new_elem) { QNodep; p=(QNode)malloc (sizeof (QNode)); if (!p) return ERROR; p->data=new_elem; if (Q->rear){ p->next=Q->rear->next; ( 1 ); } else p->next=p; ﹙ 2 ﹚; Q->size++; return OK; } int DeQueue (QueueQ,KeyTypeelem) { QNodep; If(0 ==Q->size) Return ERROR; p=( 3 ); *elem =p->data; Q->rear->next=( 4 ); if (( 5 )) Q->rear=NULL ; free (p); Q->size--; return OK; }
答案
1 2 3 4 5 (1)Q→rear→next=p (2)Q→rear=p (3)Q→rear→next (4)p→next (5)Q→rear==p 或 Q→rear→next==p或p→next==p 或 Q→size==1
第 5、6 题:面向对象编程 第 5 题为 Java 题,第 6 题为 C++ 题,一般考察面向对象各种关键字的使用。例如:
extends
super
abstract
implements
void
还可能会用到类的定义、实例化、类型定义。
本解析只收集 Java 题目,对于日常不使用这两个语言的程序员来讲,Java 显然更容易,而使用 C++ 的人也不需要看这篇文章。
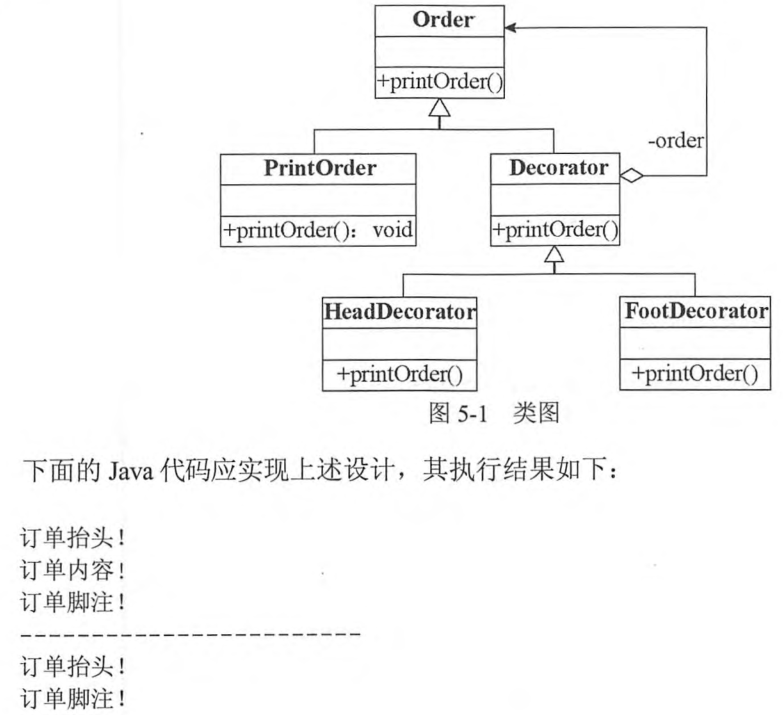
202011-5 在线购物系统需提供订单打印功能,相关类及关系如图 5-1 所示,其中类 Order 能够完成打印订单内容的功能,类 HeadDecorator 与 FootDecorator 分别完成打印订单的抬头和脚注的功能。
答案
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 (1) extends (2) this.order (3) super(order) (4) super(order) (5) super.printOrder() (6) extends (7) this.order
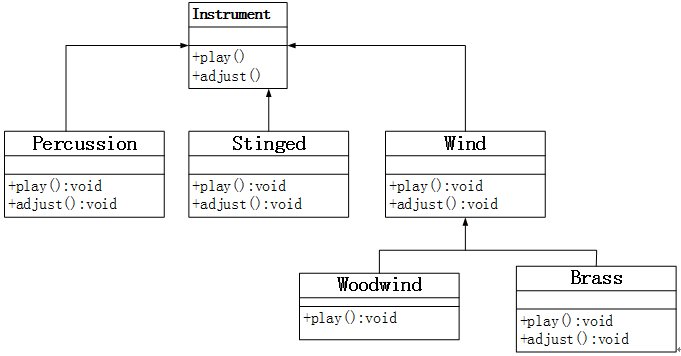
201811-5 以下 Java 代码实现一个简单乐器系统,音乐类(Music)可以使用各类乐器(Instrument)进行演奏和调音等操作。对部分乐器进行建模,其类图如图 5-1 所示,包括:乐器(Instrument)、打击乐器(Percussion)、弦乐器(Stringed)、管乐器(Wind)、木管乐器(Woodwind)、铜管乐器(Brass)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 import java.util.ArrayList;enum Note { MIDDLE_C,C_SHARP,B_FLAT; } abstract class Instrument { (1 ) ; abstract void adjust () ; } class Wind ( 2 ) { public void play (Note n) {System.out.println( "Wind.play() " +n);} public viod adjust () {System.out.println( "Wind.adjust() " );} } class Brass (3 ) { public void play (Note n) {System.out.println( "Brass.play() " +n);} public void adjust () {System.out.println( "Brass.adjust() " );} } class Woodwind extends Wind { public void play (Note n) {System.out.println( "Woodwind.play() " +n);} } public class Music { void tune (Instrument i) {i.play(Note.MIDDlE_C);} void adjust (Instrument i) {i.adjust();} void tuneAll ( ( 4 ) e) { for (int j=0 ;j<e.size():j++) { Instrument i=e.get(j); adjust(i); tune(i); } } public static void main (String[]args) { ( 5 ) music=new Music () ; ArrayList<Instrument>orchestra=new ArrayList <>(); orchestra.add(new Wind ()); orchestra.add(new Woodwind ()); music.tuneAll(orchestra); } }
答案(为了方便这里补全了完整代码行)
1 2 3 4 5 (1) abstract void play(Note n) (2) class Wind extends Instrument {} (3) class Brass extends Wind {} (4) void tuneAll(ArrayList<Instrument> e) (5) Music music=new Music()
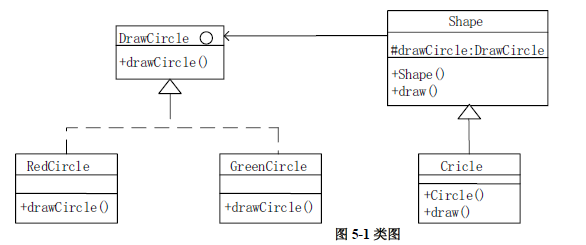
201805-5 以下 Java 代码实现一个简单绘图工具,绘制不同形状以及不同颜色的图形。部分接口、类及其关系如图 5-1 所示。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 interface DrawCircle { public (1 ) ; } class RedCircle implements DrawCircle { public void drawCircle (int radius,int x, int y) { System.out.println("Drawing Circle[red,radius:" + radius + ",x:" + x + ",y:" +y+ "]" ); } } class GreenCircle implements DrawCircle { public void drawCircle (int radius, int x, int y) { System.out.println("Drawing Circle[green,radius:" +radius+ ",x: " +x+ ",y: " +y+ "]" ); } } abstract class Shape { protected (2 ) ; public Shape (DrawCircle drawCircle) { this .drawCircle = drawCircle; } public abstract void draw () ; } class Circle extends Shape { private int x,y,radius; public Circle (int x,int y,int radius,DrawCircle drawCircle) { (3 ) ; this .x = x; this .y = y; this .radius = radius; } public void draw () { drawCircle. (4 ) ; } } public class DrawCircleMain { public static void main (String[] args) { Shape redCircle=new Circle ( 100 ,100 ,10 , (5 ) ); Shape greenCircle=new Circle (200 ,200 ,10 , (6 ) ); redCircle.draw(); greenCircle.draw(); } }
答案
1 2 3 4 5 6 (1)void drawCircle (int radius,int x,int y) (2)DrawCircle drawCircle (3)super(drawcircle) (4)drawCircle(radius,x,y) (5)new RedCircle() (6)new GreenCircle()